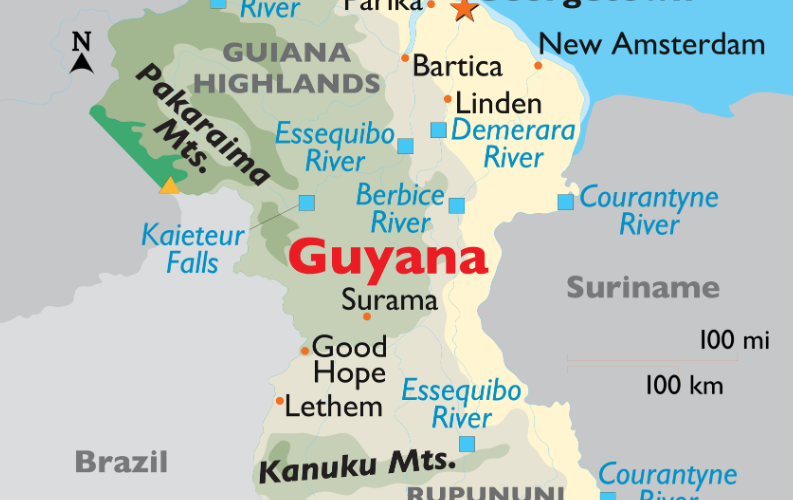
Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro has reignited tensions in the region by renewing his country’s longstanding ambitions to annex a significant portion of neighboring Guyana. In a televised address, Maduro presented a map designating Guyana’s Esequibo region as falling under the jurisdiction of Caracas, outlining plans for the creation of a Venezuelan state named Guyana Esequibo. This move has prompted widespread international concern and garnered strong responses from Guyana, the United States, and Brazil.
Venezuela has laid claim to the 61,000-square-mile Esequibo region for an extended period, a claim that Guyana has consistently rejected. The dispute dates back to an 1899 international arbitration, which Guyana argues settled the matter. However, Venezuela has contested the validity of the ruling, leading to a protracted disagreement between the two nations. Last week, the International Court of Justice urged both parties to exercise restraint and avoid actions that could exacerbate the dispute.
Maduro’s recent declarations, while currently symbolic and primarily political, have raised alarms due to their potential implications. He announced plans to grant Venezuelan citizenship to Guyanese residents in the disputed region, issue licenses for state entities such as the oil company PDVSA and metal conglomerate CVG to explore for oil, and demanded that existing energy companies, including ExxonMobil, vacate the area within three months.
Guyanese President Irfaan Ali has characterized Maduro’s actions as a “desperate attempt” to seize territories, prompting appeals for diplomatic and defense support from the United States, Brazil, and the United Nations. The U.S. State Department, in a statement, reiterated its unwavering support for Guyana’s sovereignty and emphasized the need for a peaceful resolution. In Brazil, officials have reinforced the northern border, expressing serious concerns to Venezuela and taking precautionary measures to prevent potential military actions.
While the Esequibo region holds significant oil reserves, Maduro’s push is not solely driven by economic considerations. Analysts, such as Enderson Sequera, the strategic director for Politiks, suggest that Maduro’s focus on Esequibo reflects political insecurity following María Corina Machado’s victory in the opposition’s presidential primaries. With the potential for a challenge in the upcoming elections, Sequera posits that escalating tensions with Guyana may be an attempt to rally nationalist sentiments and divert attention from internal political challenges.
Venezuela’s renewed push to annex a substantial part of Guyana has ignited international concerns and prompted responses from key nations. As diplomatic efforts intensify to address the dispute peacefully, the situation remains precarious, with potential implications for regional stability. The international community closely watches the developments, urging restraint and advocating for a resolution that preserves the sovereignty of nations involved in this historical and contentious dispute.